The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2016;29(01)
Content
[Attitude towards death, psychosomatic and pszichological status of nurses working in hospice care and oncology unit]
[Aim of the research: The aim of the research was to examine the fear of death, the attitudes towards death, the way of processing death, related to the workplace and to assess the burn out and psychosomatic symptoms among oncology nurses and hospice care workers. Research and sampling methods: To execute our research self-developed surveys were distributed online and printed (N=116) in July-August 2015, completed with a control group, as well. For data analysis we used SPSS version 19.0 with the following statistical tests: Chi square test, independent two sample t-test, Spearman rank correlation and variance analysis (p<0,05). Results: Oncology nurses had slightly more positive attitudes towards death, with significant (p=0,034) proneness to concentrate on positive events too, in case of death of their patients, and tend to attend Bálint groups more often (p=0,017), than nurses working in other unists. In the latter group psychosomatic symptoms were more frequent (p=0,032). No significant differences (p=0,234) were found between the groups in cumulative scale of fear of death. Fear of death had great effect on appearance of psychosomatic symptoms (p=0,011) and the extent of burn out (p=0,001). Conclusions: There were no significant differences in fear of death between oncology nurses and hospise care workers.]
[Care of the fistula, advantages of the monitoring and the surveillance with thermodilution technique]
[Introduction: The best choice of vascular access for haemodialysis patients is the native arteriovenous fistula (AVF). Therefore, monitoring and surveillance of vascular accesses has a high priority. Aim of the research: The aim of our study was to evaluate the AVF surveillance protocol of our dialysis clinic. Research and sampling methods: We began AVF monitoring and surveillance in our dialysis clinic in February 2003. Until May 2015 we evaluated the data of 307 patients. Results: Besides the regular physical investigation of fistulas we performed measurements of vascular access flow (Qa) with thermodilution technique. In cases of suspected stenosis we performed Colour Doppler Ultrasonography and/or fistulography. Stenosis was verified in 154 cases at 344 patients. Percutan transluminal angioplasty was performed in 241 cases at 127 patients. Creation of a new fistula was necessary only in 24 cases at 21 patients. Within the last three years the percentage of patients treated via AVF has risen from 75% to 84%. Conclusions: Regular monitoring and surveillance of vascular accesses and the timely correction of its complications are able to reduce thrombosis of fistulas and the necessity of using central venous catheters. ]
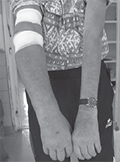
[Foot disorders of the dialyzed patients]
[In the background of increased morbidity and mortality in dialysis patients the frequent examination for foot disorders can be important. Dialysis nurses play an essential role in the recognition of these abnormalities. Registering foot disorders during regularly performed “foot visits” in our clinic. 69 dialyzed patients were examined and foot abnormalities (dry skin, calluses, fissures, abrasion, ulcers, joint deformities, fungal infections) were documented. Also peripheral pulses were examined. Calibrated tune-fork, monofilament test and neurotest were also performed. Intact, well-groomed feet were found only in 13 patients. Nail fungi were recognized in 22, dry skin and fissures in 24, abrasion and ulcus in 6 patients. In more than half of patients no peripheral pulses were palpable. Patients were given foot care tips and were admitted to specialists. Foot disorders - often in advanced state - were found in a great amount of our patients. Regular “foot visits” should become a routine examination of dialysis patients. ]
[The patients with sensory system impairment in peritoneal dialysis]
[The sensory system is responsible for perceiving information, which enables us to connect with the outside world. Its impairment could limit an individual’s chances to an equal role in society. Introduction of a special training programme that provides equal opportunities for patients with disabilities to participate in the peritoneal dialysis (PD) programme. In visually impaired patients training was not based on the visual teaching aids but on verbal communication (constant repetition, questioning). In patients with hearing loss visualisation and dexterity are in focus. Speech impediment, a condition often coexisting with hearing loss, made communication more difficult; therefore the training is built on writing, articulation and sign language. By acquiring the theoretical and technical bases of PD treatment, our patients is able to complete safe solution exchanges in their own homes. Once self-care treatment commenced, their nursing continued on an individual basis. Self-care treatment of PD patients with sensory impairment requires prudence, adequate training and aftercare; however according to our experience it does not necessarily imply a higher occurrence rate of complications. ]
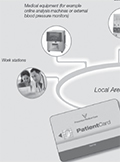
[About Therapy Data Management System (TDMS) by nurses]
[Recently, the precise management of dialysis-related documentation has become a big responsibility and burden. As a result, less time is available to perform daily nursing tasks. Therefore, our company has introduced the Therapy Data Management System (TDMS) at 10 dialysis centres. The system was developed to reduce the administrative burden and provide information to the staff about the current dialysis session. The TDMS loads the dialysis treatment prescription from the data recording programme used in our network to the dialysis machine. Two main elements are used: data base for treatment monitoring and current treatment parameters. The database for treatment monitoring is used for data input (using the computers in the unit), while the current treatment parameters are used as data input to the dialysis devices and for data documentation. Patients are identified by patient identification cards recording weight before and after the dialysis session. The programme automatically calculates the current ultrafiltration, but data can be modified if necessary. After loading and validating the parameters, treatment can be initiated. With the introduction of the TDMS the time spent for documentation was reduced by 15-20 minutes per patientshift and nurse. Dialysis can be started more easily and quickly, because the parameters of the current treatment always appear on the screen. Moreover, the risk of administration errors is reduced. This system effectively supports the daily work in clinical practice. It provides quick and easy access for all users of the management of haemodialysis patient. Keywords: dialysis, data recording, Therapy Monitor, TDMS ]
[The public catering reform in social care institutions from the care professionals point of view]
[In the European Union, the prevalence of excess weight and obesity have dramatically increased. This increase is associated with inappropriate nutrition and the lack of physical exercise, which in turn lead to an increase of chronic ill health. Consequently, this will adversely affect the quality of life, as well as the life expectancy in the long run. The health of the Hungarian population is poorer than that of other European nations. Less life years are lost in Western European countries. Poor diet plays a pivotal role among other lifestyle associated risk factors affecting health. In light of the above evidence, actions plans and programmes have been designed, as well as ministerial decrees were issued in order to sustain and improve the health of the population. There is evidence that a strong relationship exists between diet and health. Excessive dietary intake of salt increases the risk of high blood pressure. Furthermore, excessive intake of salt, carbohydrates and fat can lead to cardiovascular and malignant diseases, as well as diabetes. Obesity can be prevented by a healthy diet. However, the role of supportive environment cannot be overemphasised when it comes to the introduction of a new, healthier diet and lifestyle.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.