The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hungarian Radiology - 2009;83(04)
Content
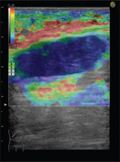
[Cervical space occupying lesions: diagnosis at sonoelastography]
[Among cervical (neck) region tumours, the thyroid lesions and the metastatic lymph nodes are the most detectable with conventional B-mode ultrasonography (US). The use of MRI and CT scans are limited because of the cost, and in case of CT, the radiation. With the introduction and constant development of sonoelastography, we have in our hands a new imaging procedure which is cheap, fast and harmless, yet giving more information to the examiner than conventional US. The elastographic examination of thyroid lesions is a more explored area than the elastographic visualisation of cervical lymph nodes. The ‘off-line’ elastography showed the highest accuracy allowing to calculate and analyse the strain index of cervical lymph nodes - strain index > 1.5 (85% sensitivity, 98% specificity) - but the ‘off-line’ processing of US elastograms is still too time consuming to be used in busy clinical settings. During the examinations of the thyroid gland both real-time and off-line processed strain imaging were used. An Italian team made a great leap forward as they standardized the degree of distorsion under the application of the external force. Then using the Ueno and Itoh elasticity score they achieved remarkable accuracy with real-time sonoelastography (P <0.0001). On the other hand only those organs are suitable for the US elastography characterization which can be slightly compressed, consequently the examination of a lesion with calcified shell cannot give useful information. Near to the pulsating arteries substantial amounts of decorrelation noise may appear and the examiner has to pay attention what structures are in the ROI box since the sonoelastography method assumes computations relative to the average strain inside the box. To detect a follicular carcinoma in the thyroid gland remains a big challenge. Despite of the limitations most researchers agree on the fact that sonoelastography is a perfect tool to use in addition to the conventional US examination. B-mode US combined with sonoelastography raised the accuracy in differentiation in all cases. With this modality it is also possible to deduce the number of cases when healthy lymph nodes or tissue peaces are taken for biopsy during FNAB.]
[Clinical significance of nuclear scans in assessing function of thyroid nodules]
[Functional and anatomical imaging plays an important role in the diagnosis and treatment of thyroid nodules presenting with continuously increasing number. In the first part of the paper the usefulness and recent trends of the classical nuclear medicine is discussed. The second part presents the interpretation of incidental thyroid lesions detected by PET-CT and the usefulness of PET in the evaluation of thyroid carcinoma.]
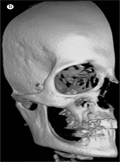
[Digital volume tomography - The use of cone beam CT in dentistry, oral and maxillofacial surgery]
[Oral and maxillofacial radiology is a subspecialty with its own field of indication. The goal is to achieve proper diagnostic image quality with the minimal amount of harmful radiation. The most common acquisition techniques are the intraoral radiograph and the panoramic radiograph which result in an overview picture of the whole dental status of the patient or the full mouth survey with the higher doses of radiation indicated for periodontological treatment. The next level is the supplementary radiograph such as occlusal radiograph, transversal tomography (some panoramic radiographs have this option), lateral cephalometric projection, submentovertex view or Waters projection, etc. More over cone beam CT acquisition or digital volume tomography as is called. In case of some described special indications CT, MRI or sometimes US acquisition can be made. In the field of three dimensional radio-diagnostics, the CT has a superior place with well-known advantages for everybody, and the usage has been limited only by the high radiation dose. The main point of the acquisition is the image quality. The load of radiation only makes the field of indication narrow. In every day practice - because of the higher radiation load of each high quality CT - the pictures passing to the doctor are preferred to take with lower resolution and wider slices although the diagnostic value of this never reaches the wanted level. This is why this new acquisition system also mentioned in the title would be better known. This system works with reasonable low radiation coupling with the possibilities of the high fidelity 3D imaging focusing on the bony structures of the head and neck region. The purpose of this article is to give a comprehensive introduction to this method in use for more than a decade. From 2006 in Hungary we also have the option to use the technology.]
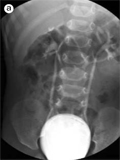
[Voiding sonocystography with ultrasound contrast material for the diagnosis of vesicoureteral reflux]
[Voiding sonocystography with intravesical administration of ultrasound contrast agent is a sensitive method to detect vesicoureteral reflux without irradiation. Depicting microbubbles in the ureters and collecting system is feasible even with very small amounts of a second-generation ultrasound contrast agent, Sonovue. The reflux is graded (I-V) in a similar manner to the system used in voiding cystourethrography. In this article a detailed description is presented.]
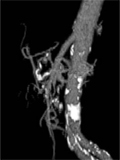
[The effect of endovascular intervention in the presence of rare celiac trunk developmental anomalies]
[INTRODUCTION - The congenital absence of celiac trunk and it’s subtotal stenosis are rare abnormalities and often recognised only during digital substraction angiography (DSA). This anomaly is significant when there is a need to perform local intraarterial chemoperfusion or chemoembolisation of malignant hepatic tumours. In these cases the liver is supplied with arterial blood through the superior mesenteric artery and the gastroduodenal arch. The direction of blood flow in the common hepatic artery is changed ensuring the flow to the splenic and left gastric artery. In such circumstances it is not possible to obtain local chemotherapy. CASE REPORT - Two male patients (61 and 75 years old) are reported. Both patients were candidates for chemotherapy due to hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In these two cases the planned therapy was impossible because of a stenosis of the celiac trunk in one, and atresia of the celiac trunk in the other. CONCLUSION - The recognition of vascular anomaly prior to endovascular intervention significantly affects the planning of the therapy.]
[Initial experiences with upper limb MR-angiography]
[INTRODUCTION - Cimino fistula is created for chronic hemodialysis. As a common complication steal syndrome may occur. Till recently, color Doppler and catheter angiography were the gold-standard diagnostic tools. We have performed MR-angiography of the upper limb to replace the more invasive conventional angiography in patients with poor general condition. PATIENT AND METHODS - A case of a 64 years old female patient with known type II diabetes is presented. Due to azotemia, the patient has received hemodialysis for 24 months, via a left upper limb fistula. This fistula occluded, and the Cimino-fistula was later created on the right arm. This new fistula demonstrated steal syndrome, and required formal ligation. In the meantime a necrotising drygangrene of the 4th and 5th digits was recognised. This required an emergent conventional angiography, but due to the unavailability of accessible artery, MR-angiography was performed. 1.0 mmol/ml concentration gadobutrol (Gadovist 1.0, BayerSchering, Berlin) was used to reduce the chances of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in this patient with poor renal function. CONCLUSION - Correctly performed MR-angiography to examine the possibility of steal syndrome in patients with a Cimino fistula can be a feasible alternative. The advantages of the procedure include its minimal invasiveness, no ionizing radiation and the risk of iodine-based contrast material nephrotoxicity. Also, as compared to digital substraction angiography, with MR-angiography we obtain a high-resolution, isotrope voxel-sized 3D acquisition which can be better read in many different planes. As a drawback, currently on-location intervention cannot be performed, if needed. Also, the waiting periods may be long.]
[Diagnosis of ovarian torsion through the ultrasound and in the operating theatre - An audit and review of the current diagnostic modalities]
[INTRODUCTION - This audit was carried out to assess the usefulness of ultrasound in the diagnosis of adnexal torsion in pediatric and adolescent patients, and to demonstrate any ultrasound characteristics which are predictive of ovarian torsion in this population. PATIENTS AND METHODS - Retrospective review of ultrasound reports, operative reports, and medical records for 17 pediatric patients treated at BAZ-County University Hospital, Miskolc, was performed. The patients had presented to the pediatric surgery with complaints of abdominal pain between August 2000 and August 2008, and underwent an abdominal/pelvic ultrasound prior to going to the operating room for surgical management. All ultrasounds were categorized regarding the presence or absence of adnexal torsion. Other sonographic parameters included were: the mass size, description, and the presence of signs associated with adnexal torsion (presence and arrangement of ovarian follicles, presence of free fluid in the pelvis, and the presence or absence of arterial or venous flow by color Doppler to the ovaries). Surgical and pathological findings were also studied. RESULTS - All 17 patients in this review were surgically confirmed cases of torsion. 14 (82%) of the torsions occurred on the right side, 3 (18%) on the left side. Ultrasound described 8 adnexal masses with torsion as cystic (n=8, 47%). Pelvic fluid was present in nine patients (53%). Of 10 patients in which follicles were noted, follicles were observed to be peripherally displaced in seven (41%). Only two patients (12%) underwent laparoscopic surgery, remaining received open surgery. On evidence of torsion in the operating room, detorsion was performed in all cases. Finally, tubal cystectomy was performed in 2 (12%), ovarian cystectomy in four (24%), oophorectomy in two (29%), salpingooophorectomy in 6 cases (35%), and oophoropexy was performed in three cases (2%). The majority of pathology in those with confirmed torsion were hemorrhagic cysts in 10 cases (59%), paratubal cysts in three cases (18%), and teratomas in one cases (6%). No histologies were sent for three patients who received oopheropexy. 13 patients (76%) with torsion had adnexal masses greater 5 cm. The duration of complaints prior to treatment was also an important factor: Generally patients with more than one day long complaints underwent oophorectomy, exception to this was a case with intrauterine torsion. CONCLUSIONS - In our audit, patients with adnexal masses greater than 5 cms were more likely to have torsion than those patients with masses less than 5 cms.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.