The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hungarian Radiology - 2008;82(07-08)
Content
[Radiology of pancreas: review from the last year - Gastro Update 2007]
[PURPOSE - To demonstrate the recent results in radiological diagnostics of pancreas, and the actual place of the imaging and interventional methods. METHOD - Systematic review of the most recent articles from the last year in the following subjects: acute, chronic and autoimmune pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer and other tumors, PET and special imaging problems in pancreas transplantation. RESULTS - Annually, experience in pancreatic diagnostical methods are accumulating rapidly. Therefore, there is a continuous change in the examination algorithm with new diagnostic and therapeutic modalities making their way into the daily routine. Some of the algorithms become obsolete within a few years and their further application is considered mismanagement. Some other methods become obligatory steps in the diagnostics. These are the reasons why up-to-date knowledge of the literature is mandatory.]
[Role of contrast enhanced ultrasound in clinical practice]
[Ultrasound contrast agents consist of micro bubbles which can be visualized during their short intravascular and parenchymal transit time. An US system with special software, a small amount of intravenous contrast agent and a skilled operator is necessary to produce a successful study. This method can also be introduced into the clinical practice in our country. Careful indications and well performed studies can reduce the number of unnecessary CT and MR studies and biopsies. Contrast enhanced US has special clinical significance in the detection and characterization of focal liver masses, monitoring drug and local treatment effects of different abdominal tumors and in the case of injury of abdominal parenchymal organs.]
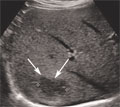
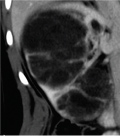
[Evaluation of cystic renal masses with MDCT]
[Modern CT and MRI scanners can give an exact and rapid diagnosis in the case of most cystic renal masses. Dilemma in their diagnosis is whether or not the changes need surgical intervention. The question of follow-up is decided with the use of the Bosniak classification. To characterize the cystic changes excellent quality, multiphasic MDCT examination is necessary with the following parameters: 80-120 mls. of non-ionic iodinated intravenous contrast material given with an injector at 3 ml/sec flow-rate with saline flush technique, unenhanced and post-contrast scans obtained at 35 and 70 seconds, with more scans at 120-300 seconds, as deemed necessary. A collimation of 16x1.5 mm with an overlap of 50% should be aimed for. Through the primary data we perform a reconstruction of 2 mm, with an option to create volume-rendered image sin the post-processing phase, as necessary. With the help of this CT protocol we can measure the different criterions of Bosniak classification in the cystic masses like minimal, smooth or irregular wall thickening, with or without enhancement. We can recognize hairline thin or thickened septa, fine or irregular (thick or nodular) calcifications, solid component with or without contrast enhancement. Using these criteria each cystic mass can be assigned to a Bosniak cystic category (I, II, IIF, III and IV)]
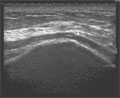
[High resolution sonography for the examination of peripheral nerves]
[High-frequency sonography is an important method for the imaging of the peripheral nerves, even though it is rarely used. For the examination of superficially located nerves, currently available transducers with frequencies between 12-17 MHz offer a better axial resolution than even MRI. Sonography is superior to MRI especially for the examination of nerves of the upper extremity. Main indications for the sonography of the nerves are entrapment syndromes, traumatic injuries of the nerves, tumors, polyneuropathies and sonographically-guided interventions. The sensitivity of sonography and electrophysiology in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome and cubital tunnel syndrome are comparable. The combination of ultrasonography with electrophysiological studies increases the diagnostic yield in carpal and cubital tunnel syndromes. Sonography provides information for planning of peripheral nerve surgery and is helpful in evaluating postoperative complications. In selected cases, sonography can detect nerve lesions that require operative therapy earlier than electrophysiology. With technical enhancements, highfrequency ultrasonography is gaining increasing importance in the routine diagnostics of peripheral nerves lesions.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.