The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hungarian Radiology - 2008;82(05-06)
Content
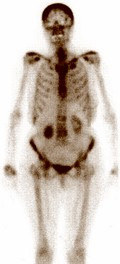
[Radiological diagnostics in bone metastases]
[Imaging plays a crucial role in defining bone metastases, and thus, therapy planning. We are responsible for accurate data collection, pre-treatment evaluation, evaluation of therapy response and post-treatment evaluation. Precision highly depends on the expertise and experience of the evaluating radiologist, and therefore, being familiar with the latest literature is essential. The bone status can be detected well by bone scan, analysed by conventional X-ray examination and by the cross sectional digital imaging modalities. The whole body PET/CT functional imaging is becoming increasingly popular in the metastatic workup of patients and for monitoring response to therapy. MRI has been found to be the most accurate method for bone metastasis in most comparative evaluations in the literature. This article is a review of the latest papers focusing on the clinical significance of the imaging results in bone metastasis diagnostics.]
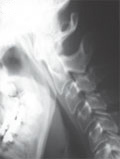
[Rheumatoid arthritis: significance and methodology of cervical spine X-rays in everyday practice]
[Cervical spine joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis may lead to progressive vertebral instability. It is a severe risk factor for cord compression, which may even lead to sudden death. Many patients with atlantoaxial subluxation may have no symptoms referable to the neck. True degree of subluxation may occur during anaesthesia when the neck muscles are relaxed and protective spasm is absent. The cervical deformities can be visualised on conventional, transoral and functional lateral view in the flexion and extension positions of the neck. The aim of our study is to demonstrate the usefulness of cervical dynamic X-ray for patients suffering from rheumatoid arthritis. This is the first classical radiological imaging method in the diagnosis and in radiographic follow-up. It is a very important method in the preoperative evaluation to prevent definitive neurologic injury. We describe the method for screening, measuring and grading cervical subluxations and instability in our everyday routine.]
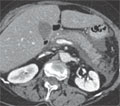
[Role of radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of malignant liver tumors - Possibilities and limitations]
[Radiofrequency tumour therapy is a minimally invasive procedure. It has been used in several specialities independently of the type and location of the tumour, and has shown its worth. In primary hepatic malignancies, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a curative procedure. Recent publications reveal that hepatocellular carcinomas which were of cirrhotic origin and not larger than 5 cm have shown similar responses to both RFA and surgery. In cases of metastatic hepatic tumours, RFA showed slightly poorer results as compared to surgery. But, in tumour foci less than 3 cm or in patients in whom the perioperative risks were high (and they presented with tumor foci less than 3 cm and 3 foci), RFA proved to be a better alternative to surgery. RFA, when used percutaneously, is a cheaper procedure as compared to surgical resection. It can be performed on an out-patient basis with a maximum of 24 hours of observation. Local anesthetic or slight sedation may be employed. Greatest advantage of RFA is its ability to cause tumour degradation. Its results are not well known in our country. Under the existing financial system, RFA is not feasible.]
[Use of plain and intravenous contrast material multidetector CT examinations in acute abdomen]
[Through most of Europe, multidetector computed tomography is used as the first-line modalitiy for examining the acute abdomen. Acute abdominal pain, symptoms referring to abnormal bowel movements, gastrointestinal bleeding, worsening general state, and other typical clinical signs require quick and precise diagnosis since these conditions are frequently life-threatening. The sensitivity and specificity of CT examinations have significantly improved due to the development of the machinary. Thus, the scope of indications are also expanding. Almost all acute abdominal disorders, that may lead to an acute surgical procedure, can be diagnosed with the help of multidetector CT. Unnecessary surgical procedures, the risk to the patients and also the cost of hospitalization can be reduced using multidetector CT examination.]
[Forces exerted on the plaques during in vitro measurements by various carotid stent delivery systems and embolic protection devices]
[PURPOSE - During the endovascular treatment of internal carotid artery stenosis, one of the most important aspects is reducing of embolic complications. Degree of embolization may be influenced by the force exerted by stent delivery systems and embolic protection devices. We assessed the force emersion produced by various devices on vessel walls and plaques. MATERIAL AND METHOD - Six different commercially available devices were investigated. The force load on vessel wall was measured in a carotid model with vessel angulations of 25, 50 and 75 degree, respectively. The IDTE 2000 CE marked measurement system was used. A transparent, flexible PVC tube was used as a model of the carotid bifurcation, which was 6 mm in width, 1.5 mm wall thickness and 12 mm length. 75-85% stenosis were created in it. The measured data were evaluated and different conclusions were drawn. RESULTS - Forces exerted on vessel walls varied widely among different stent delivery systems. The magnitude of force exertion caused by stent delivery systems significantly exceeded that caused by protecting devices. Protecting devices showed only 30% increase in vessel load at angulation of 75 degrees compared to those at 25-50 degrees. Above 50 degrees of vessel angulation the forces exerted by stent delivery systems considerably increases. CONCLUSIONS - Our results showed that selection of the most proper stent can contribute to decrease in the load of vessel wall. Protecting devices exert significantly lower forces than stent delivery systems, therefore, it seems to be a better choice to advance a protecting device before introducing a stent delivery system. If the vessel angulation exceeds 50 degrees, endarterectomy should be considered, because the vessel wall load will increase radically in that case.]
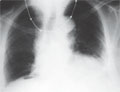
[The bubble-sign of spontaneous pneumoperitoneum]
[INTRODUCTION - Pneumoperitoneum is a reliable indicator of serious underlying damage. There are four etiologic categories of extraluminal-intraperitoneal gas collections: spontaneous, iatrogenic, traumatic and criminal perforations. The erect posteroanterior chest radiograph is the most sensitive plain film projection for detecting pneumoperitoneum and it may show 0.5-1 ml free abdominal gas when meticulous radiographic techniques (lateral, oblique, air-gap, lordotic, inspiratory and expiratory exposures) are used. The appearances of extraluminal gas collections are specified by physical rules and individual preferences. The bubble-sign is an uncommon, pathognomonic phenomenon. CASE REPORT - A case of an 86 years old female patient with spontaneous pneumoperitoneum, diagnosed on the basis of the bubble-sign is presented. On erect, lordotic inspiratory chest film, right medial inversion of diaphragm, left pleural effusion, emphysema, cardiomegaly and aortectasia were observed. The bubble-sign and hydromediastinum became evident in the right phrenicocostal angle on expiratory view. Our patient expired before the surgical intervention.The postmortem demonstrated double peptic duodenal ulcers; the older ulcer had penetrated and encapsulated in the hepatoduodenal ligament, while the more recent one perforated through the intraperitoneal space. CONCLUSION - Routine upright chest films are valuable screening tools for uncommon signs of pneumoperitoneum, also.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.