The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hungarian Radiology - 2005;79(02)
Content
[Radiological diagnostics of the pancreas neoplasms - Onco Update 2005]
[Authors reviewed the recent results of pancreas tumour radiological diagnostics and the place of the imaging and interventional methods. Systematical review of the most recent articles were summarized (July 2003-December 2004) in the following subjects: the etiology and clinico-pathology, general diagnostic and therapeutical questions of early pancreatic neoplasms, abdominal ultrasound, computed tomography, multidetector computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, MR-cholangiopancreatography, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, endoscopic ultrasound, intraductal ultrasound, endoscopic ultrasound-guided cytology, percutaneous biopsy, positron emission tomography, positron emission tomography - computed tomography, special pancreatic tumours. Experiences about the pancreas diagnostic methods are accumulating year-to-year rapidly. Therefore the current examination algorithm is changing continuously. New diagnostic and therapeutic modalities are entering in the daily practice. These are the reasons why the up-to-date knowledge of the literature is mandatory.]
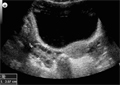
[Radiologic diagnosis of the diseases of the pediatric gynecology]
[The basic examination of the pediatric pelvic organs is the transabdominal ultrasound which provides useful information about the anatomy and the pathological changes and in the vast majority of cases it is sufficient for treatment planning and to establish the diagnosis. Additional examinations are needed in case of complex developmental anomalies, in suspition of tumor, in staging and follow up examinations of tumors. Among the modern imaging methods the use of CT and MRI can be considered. The authors described the most frequent diseases in their practice and gave a brief overview on anatomical and physiological basics which is necessary for the exact interpretation of the examinations.]
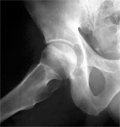
[Early detection of adult femoral head necrosis]
[Adult avascular femoral head necrosis is common in young adulthood, and in 80% of cases affects male patients. The disease is bilateral in 40-80 %, and it may take several years to develop on the contralateral side. Late diagnosis and lack of early therapy can cause progressive disease and finally movement restraint. The diagnosis in early stage is crucial for choosing the most effective strategy in therapy. It is important to be aware of pathogenesis, clinical course and the differential diagnostic options of the disease, and these should be associated to the diagnostic findings at different imaging modalities. Based on this concept, we conclude that MR examinaton is the method of choice for the early (reversible) stage assessment. MRI of the hip is also able to evaluate and follow up the healthy contralateral side without further strain.]
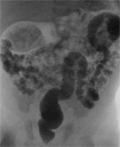
[Dudoenum obstruction caused by duodenal diaphragm]
[INTRODUCTION - Duodenum obstruction is a rare gastrointestinal developmental anomaly. It may be complete or incomplete. The incomplete or intrinsic form is often caused by an intraluminal membrane or web duodenal stenosis. The passage is existed with the help of a small perforated lake. Clinically the leading sign is the vomiting. CASE REPORT - A three days old baby admitted because of vomiting. Abdominal X-Ray and US could not found any reason of vomiting but the gastrointestinal contrast series had diagnostic value. Surgery proved the radiological diagnosis. CONCLUSION - For the diagnosis the conventional XRay and ultrasound is not sufficient in every case, the gold standard is the gastrointestinal contrast examination.]
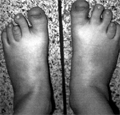
[Czech dysplasia metatarsal type]
[We report a further female patient with the recently described new bone disease, Czech dysplasia metatarsal type. Czech dysplasia metatarsal type (CDMT) is an autosomal dominant debilitating disorder. Its constant phenotypic trait is hypoplasia/ dysplasia of the 3rd and/or 4th toes. “Congenital hip dysplasia” or “hip disease” is commonly evoked in the family history. The clinical course may be severe, incapacitating the patients early in life, or progress slowly with increasing hip and spine pain. This girl's phenotype and radiographic findings are similar to the seven previously reported cases.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.