The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hungarian Immunology - 2008;7(01-02)
Content
[The role of endothelium, cell migration, chemokines and angiogenesis in inflammatory rheumatic diseases]
[Endothelial cells, leukocyte-endothelial interactions and angiogenesis are highly involved in the pathogenesis of inflammation and thus in that of inflammatory rheumatic diseases. As this research area is very progressive, one needs to review novel molecular mechanisms and new therapeutic approaches in this respect. Authors review the most important functions of endothelial cells, the process of leukocyte extravasation, tissue infiltration and their cellular and molecular basis. Endothelial cells themselves produce a number of inflammatory mediators including interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, IL-8, chemokines and others. Among cell adhesion molecules, β1 and β3 integrins, as well as E-, L- and P-selectins and their respective ligands have been implicated in leukocyte-endothelial adhesion. In recent years, numerous inflammatory mediators, cytokines, chemokines and proteases have been implicated in angiogenesis and angiostasis. Hypoxia, the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-angiopoietin system and mechanisms driven by β3 integrins are of major importance during angiogenesis. Significant amount of data have become available of the regulation of cell adhesion, migration and neovascularisation. Adhesion, chemokine and angiogenesis research has important clinical, practical aspects for antirheumatic and anti-cancer therapy. VEGF antagonists, anti-integrin antibodies, chemokine and chemokine receptor inhibitors, as well as thalidomide are currently in the first line of development.]
[Kinetic measurement on flow cytometer simultaneous monitoring of intracellular progresses]
[INTRODUCTION - Flow cytometry provides an opportunity for real-time monitoring of intracellular processes in several cell populations simultaneously. Cells stained with specific fluorescent dyes are sequentially measured during kinetic FACS measurements. Fluorescent light signals obtained in cells are recorded and analyzed to describe the alteration of the investigated parameter(s) over time. The use of kinetic FACS assays is not spread as there was no mathematic algorithm to characterize objectively the distribution of data and kinetic changes. MATERIALS, METHODS, RESULTS - We developed a new approach which fits functions to measured data sets, describes the statistical distribution and forms a basis for statistical comparison between individual kinetic measurements. We created two FACS assays on BD FACS Aria instrument. The first one monitors calcium flux, generation of reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial membrane potential, while the second one monitors mitochondrial calcium flux, nitric oxide generation and plasma membrane potential in CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes simultaneously before and after the administration of a lymphocyte activator. CONCLUSIONS - This technique may be used to investigate purposes (i.e. to test the impact of any agent (such as immunmodulatory drugs) on cellular processes in lymphocytes) and to diagnostic purposes (i.e. to test the alteration of lymphocyte activation characteristics in disease).]
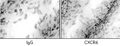
[MCP-1 (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1) G/A and T-bet (T-helper promoter factor) C/G polymorphisms in primary Sjögren’s syndrome and systemic lupus erythematosus]
[INTRODUCTION - Monocyte chemoattractant protein- 1 (MCP-1) is a β-chemokine involved in the attraction and accumulation of mononuclear granulocytes towards the site of inflammation. One of the transcriptional factors of T-cells is called T-bet. PATIENTS AND METHODS - The authors investigated the MCP-1-2518 G/A and T-bet 310 C/G (His33Gln) polymorphisms evaluating the distribution of the specific genotypes in 45 patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS), 51 patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and in 320 healthy blood donors as the control group. MCP-1-2518 G/A and T-bet 310 C/G polymorphisms were detected with molecular genetic methods from the purified genomic DNA. RESULTS - The frequency of the MCP-1-2518 AG heterozygous genotype decreased tendentiously only in SLE patients, while the frequency of the MCP-1 AA homozygous genotype increased comparing to the control group (13.7% vs. 5.9%; Pearson’s χ2 test=6.125, ns.). Analyzing the genotype frequency for the MCP-1 wild (GG) and AA homozygous genotypes in pSS group, the MCP-1 AA homozygous genotype proved to be more frequent comparing to the control group (82.8%:17.2% vs. 90.7%:9.3%; Pearson’s χ2 test 1.755, ns). These relations showed only tendentious association in the SLE group (81.6%:18.7% vs. 90.7%:9.3%; Pearson’s χ2 2.811, p=0.094, ns.) There was not any significant correlation between the investigated MCP-1- 2518 G/A and the T-bet 310 C/G polymorphisms and the TNF-α -308 G/A and -238 allele polymorphisms. The frequency of T-bet was equal in relation with heterozygous (CG) to wild CC genotype in the investigated two autoimmune disorders. The GG homozygous genotype for T-bet could not be found in SLE and pSS groups, likely to be a protective factor. CONCLUSIONS - The above mentioned polymorphisms didn’t show any significant correlation with TNF-α -308 and -238 allele polymorphisms. The further research of the MCP-1 G/A and T-bet C/G polymorphisms is important, because of their possible prognostic importance for SLE and pSS.]
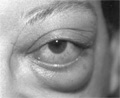
[Pseudolymphoma orbitae]
[INTRODUCTION - Pseudolymphoma orbitae is a rare and difficult entity. The cooperation of the pathologist and clinician is needed to properly manage the patient. CASE REPORT - The authors report the case history of a 38 years old male patient. His disease started at the age of 30. He was previously treated with allergic rhinitis. No definitive diagnosis was made for eight years. Several surgical biopsies were made from nasal mucosa, but no specific histologyical diagnosis was applicable. At the age of 30 he developed an unilateral exophthalmus on the left side. Thyroid associated ophthalmopathy was ruled out several times with laboratory analysis. High dose methylprednisone therapy was repeatedly given with limited results. At the age of 34 orbital CT and MRI scan confirmed the pseudotumour orbitae already compressing the optical nerve. Laboratory analysis again ruled out thyroid associated ophthalmopathy. Churg-Strauss syndrome, Wegener’s granulomatosis or Sjögren’s syndrome could be ruled out. A bone marrow trephine biopsy excluded systemic hematological disease as well. A biopsy was performed from the retrobulbar mass again, which confirmed the lymphoid hyperplasia with B-cell dominance. High dose methylprednisone and local irradiation resulted only moderate decrease of the mass, so systemic chemotherapy was started using CVP (cyclophosphamide, vincristin, prednisone) then CHOP (CVP + anthrycycline) polychemotherapy for eight cycles and subcutaneous interferon-α for 20 months. CONCLUSIONS - This resulted a complete regression of the disease, and the patient is well for 48 months now.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.