The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hungarian Immunology - 2005;4(01)
Content
[Pathomechanism of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis]
[The two archetypes of inflammatory bowel diseases, Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) have a considerably high prevalence and chronic morbidity, and thereby a striking public health relevance amongst the maladies involving the gastrointestinal tract. Unveiling their pathogenesis can be the key for the development of successful therapeutic approaches. Our view of these diseases has undergone radical changes in the past few years, and the latest discoveries have shed new light upon their pathomechanism. A multifactorial view is appropriate when explaining their pathogenesis, although certain factors are seemingly of particular importance.]
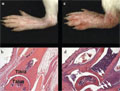
[Experimental arthritis model]
[Animal models of experimental arthritis can be used to understand pathophysiology of the arthritic processes in patients and provide opportunity to develop new therapeutic approaches. The animal models can be divided into different categories based on the pathomechanism of the model and on the features that resemble human inflammatory joint diseases. This review provides an overview of the most widely used types of experimental arthritis models emphasizing their advantages and limitations in the basic arthritis research.]
[Immune-dysfunctions in patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma being in a long lasting complete remission]
[OBJECTIVES - Immunosuppression has long been known to be associated with Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The authors report on immunologic abnormalities with special focus on cellular immunity in patients with Hodgkin’s disease in complete remission. METHODS - We determined the proportion of the lymphocytes subpopulations, activated T cells, CD4+/CD25+ suppressor T cell population and intracytoplasmic cytokines by flow cytometry. The soluble cytokines were measured by classical ELISA technique. RESULTS - Based on lymphocyte cell surface antigen expression the subpopulations were as described in the literature, however a unique elevation of CD4+/CD25+ cell fraction was detected. The decreased amount of IFN-γ in the serum suggest Th2 dominance, but reduced intracellular IL-4 production in both CD4+ and CD8+ cells results from Th1 dominance. These results somewhat contrary but can not be completely compared as in vivo and in vitro techniques used for the analysis are not identical. However a constant elevation concentration and expression of IL-10 and TGF-β is observed. CONCLUSION - These alterations may reflect the existence of an immunosuppressive state also in the peripheral blood of Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients not only in the lymph nodes.]
[Functional measurements of the hand’s circulation in Raynaud’s patients]
[INTRODUCTION - In patients presenting with isolated tissue perfusion disturbance without large vessel involvement the examination of hand microcirculation is of major importance. In our study we present the results of three examination methods used for hand perfusion monitoring which measure the tissue microcirculation in different depths. PATIENTS AND METHODS - We examined 58 primary Raynaud's patients using capillary microscopy, laser doppler perfusion imaging and hand perfusion scintigraphy with Tc-99m-DTPA. From our patients 38 were smokers, 42 patients frequently suffered from headache. For the validation of our laser Doppler results we involved into the study also 16 non-smoker healthy volunteers. For the standardisation of the results the studies were performed in a climatised room. During the laser examination we performed and analysed also the post-occlusion hyperaemia test. RESULTS - In the majority of our patients no morphological alterations were found with capillary microscopy. In primary Raynaud’s patients the perfusion values measured with laser-Doppler scanner in basic condition were significantly lower both in fingers’ and palm’s regions compared to healthy controls. In the primary Raynaud’s group the smokers had significantly lower hyperaemic response than the non-smokers and we measured also significantly lower FPR (finger-to-palm ratio) values with hand perfusion scintigraphy. Both with laser doppler imaging and hand perfusion scintigraphy there was no difference between the values measured in patients with or without headache. CONCLUSIONS - We consider of benefit the functional examination of hand circulation in all diseases involving the hand microcirculation.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.