The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Hungarian Immunology - 2003;2(04)
Content
[Models of immune recognition: presence and future]
[The prevailing theories of immune recognition for over 50 years were based on the idea that the immune system functions by discriminating self and nonself. Since the self-nonself theories failed to explain a number of immune phenomena new models were suggested, such as the ”infectious nonself” and the ”danger” models. The review outlines and compares these models of immune recognition.]
[Pathogen-associated molecular pattern of bacteria and its recognition by the host]
[Pathogen-associated molecular pattern of bacteria is determined by a molecular complementarity between the host and the microorganism. The process of pathogenesis is initiated through recognition of bacterial components or products by receptor molecules of the host organism. Constant structural components like the lipopolysaccharide in Gramnegative and lipotheichoic acid in Gram-positive bacteria are recognised by receptor molecules present in a wide range of host species, and in this way they elicit interactions and pathologic processes generally present in bacterial infections. At the same time accessorial components (adhesins, capsular material) or extracellular products (exotoxins, enzymes) mediate specific interactions which determine host species or organ specificity according to the molecular structure of the virulence factor and the specific host/organ receptor. The pathogen-associated molecular pattern is subject to changes as genom plasticity in bacteria allows evolution of virulence through recombinations and pathoadaptive mutations. Actual expression of accessorial virulence factors is frequently governed by complicated regulatory mechanisms as an adaptative response to environmental stimuli present in the host.]
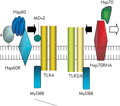
[The role of Toll-like receptors in the early steps of innate inmunity. Signaling pathways, responses on the level of cells and the organism]
[The family of Toll-like receptors are currently one of the most intensively studied group of proteins in immunology. Their ligands include a wide range of microbe-derived molecules, they are expressed on a number leukocyte populations and regulate immune responses very efficiently. In this review we characterize known common and individual signaling pathways of the receptor family and their interference with effects of other receptors, and describe the outcome of TLR signaling on the level of the cells and the organism.]
[Multiple interactions between heat shock proteins and innate immunity]
[Heat-shock proteins play essential roles in all living cells and their structure is highly conserved during evolution. Their expression is up-regulated in response to diverse stress stimuli and HSPs may function as a marker of danger. There are multiple processes in innate immunity to recognize HSP. Due to their strong recognition and conserved nature HSPs are immunodominant antigens in most of the bacterial infections and are therefore frequently key players in infection induced autoimmunity. The antigenic picture of HSPs is coded in the immunological homunculus in mammalian organisms and the maintenance of regulating autoimmunity protects against self-damaging processes.]
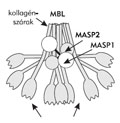
[The role of the complement system in the primary recognition processes and in the regulation of adaptive responses]
[It is known for long that the complement system present in blood and other body fluids is able to kill pathogenic microbes as a result of activation. It is also well-known that certain complement components enhance phagocytosis by opsonizing foreign substances. In addition to these roles, recent experimental results point to novel functions of certain complement proteins/receptors, namely to their contribution to the development and regulation of the adaptive response and their capacity to influence the interaction between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. During these processes certain proteins of the complement system recognise non-self structures and distinguish them from the body’s own constituents/cells. This step initiates the activation of the cascade generating several biologically active molecules, which then regulate various immune reactions.]
[Our archaic heritage: the innate immunity. The cellular immunity of Drosophila]
[Authors describe the essentials of the cellular immunity of Drosophila. They describe the Drosophila CD system, the main blood cell lineages and a blood cell differentiation model based on the expression of the CD antigens.]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.