The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Clinical Neuroscience - 2016;69(11-12)
Content
[Recommendation for treatment options in advanced Parkinson's disease]
[The treatment of advanced Parkinson’s disease is challenging for both physicians and caregivers. The device-aided therapies need expertise and dedicated hospital centers. In this summary we have concluded the available data and recommendation for the treatment options in advanced Parkinson’s disease and adopt them to the daily care in Hungary. ]
[Behavioral and cognitive profile of corpus callosum agenesia - Review]
[Introduction - Agenesis of corpus callosum is a relatively frequent congenital cerebral malformation including dysplasia, total or partial absence of corpus callosum. The agenesis of corpus callosum can be occured in isolated form without accompanying somatic or central nervous system abnormalities and it can be associated with other central nervus system malformations. The behavioral and cognitive outcome is more favorable for patients with isolated agenesis of corpus callous than syndromic form of corpus callosum. The aim of this study is to review recent research on behavioral and social-cognitive functions in individuals with agenesis of corpus callosum. Developmental delay is common especially in higher-order cognitive and social functions. Methods - An internet database search was performed to identify publications on the subject. Results - Fifty-five publications in English corresponded to the criteria. These studies reported deficits in language, social cognition and emotions in individuals with agenesis of corpus callosum which is known as primary corpus callous syndrome. Discussion - The results indicate that individuals with agenesis of corpus callosum have deficiency in social-cognitive domain (recognition of emotions, weakness in paralinguistic aspects of language and mentalizing abilities). The impaired social cognition can be manifested in behavioral problems like autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.]
[The role of zonisamide in the treatment of women with epilepsy]
[The antiepileptic drugs can effect fertility, development of gynecological diseases and occurence of sexual problems. They can cause a number of “cosmetic” problem and also influence the selection of safe contraceptive method. Many antiepileptic drugs can cause congenital malformations or affect the new-born child’s psychomotor and cognitive development, therefore during pregnancy should be treated with extreme caution in women with epilepsy. Most types of epilepsies accompany the patient through their whole life. Women spend almost the third of their lives after menopause and - due to the formation of associated diseases as well - this period is also special. According to the 2013 recommendation of International League Epilepsy (ILAE), zonisamide is one of the first-line antiepileptic drugs in focal epilepsy. In my review I discuss women’s epilepsy in the viewpoint of the application of zonisamid. ]
Patient characteristics and the effects of intravenous immunoglobulin in patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome
Purpose - The purpose of this study is to determine the diagnosis- and treatment-related characteristics in Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) and to evaluate the effects of early intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) treatment on disability, mortality and prognosis. Materials and methods - Adult patients who were diagnosed with GBS in our clinic between January 2000 and January 2014 were retrospectively scanned. While the patients undergoing IVIg treatment were included in the study, the other neuropathic diseases were excluded. Patients were divided into two groups based on the administration time of the IVIg treatment; Group 1 (<7 days) and Group 2 (≥ 7 days) Group 1 consisted of patients undergoing IVIg treatment within 7 days after presentation of symptoms and Group 2 consisted of patients undergoing IVIg treatment on and after 7th day following presentation of symptoms. The scores from Hughes Functional Grading Scale (HFGS) on admission and one month laterwere recorded in all patients in order to evaluate the disability and prognosis in terms of demographic and clinical laboratory characteristics. Results - In this study, 49 GBS patients were included (31 patients in Group 1 and 18 patients in Group 2). Demyelinating form of GBS was determined in 22 (44.8%) patients.). While there was no difference between both groups (p: 0.288, p: 0.762, p: 0.693 respectively) in terms of intensive care and rehabilitation requirement and progression, only 2 patients in Group 1 died. While HFGS mean score on admission in all the patient groups was 3.27±0.974, their HFGS mean score at month 1 was 2.53±1.226. There was no difference between the groups in terms of HFGS mean scores on admission and at month 1. Within each groups, there was a significant improvement between initial (on admission) HFGS scores and HFGS scores acquired at month 1. Conclusion - In this study, demyelinating form was more frequent than axonal form. A total of 2 g/kg dose of IVIg treatment administered for 5 days as a standard in GBS patients ensured a significant improvement on both disability and early and late administration and early administration of the treatment does not lead to any difference in intensive care unit and rehabilitation requirements.
How to minimize the risk for headache? A lumbar puncture practice questionnaire study
Background - To lower the risk for post lumbar puncture (LP) headache the American Academy of Neurology (AAN) recommended using small bore atraumatic needles together with stylet reinsertion in a report from 2005. It is unclear whether these recommendations are followed or not. Objectives - To investigate the diagnostic LP preferences with respect to the AAN guidelines among neurologists by use of a short online questionnaire, and to review previously published literature on the subject. Results - A total of 284 respondents who performed diagnostic LPs completed the questionnaire. Almost half (41%) answered that they always use atraumatic needles. The most common reason (73%) for not using atraumatic needles was that these were not available. Less than half of the respondents who performed LPs had knowledge about the AAN guidelines for diagnostic LPs, and 48-76% agreed with the different recommendations therein. Five previously (1998-2015) published studies investigating LP practice among neurologists were identified. The reported frequency of atraumatic needle use (always/routinely) varied between 2 and 16%. Discussion - Atraumatic needle use was more common in this study compared with previous publications. There is still skepticism regarding some of the AAN recommendations, and needle availability appears to be the most important factor preventing atraumatic needle use. To increase the use of atraumatic needles we may perform additional studies investigating their potential benefits, and arrange training sessions for neurologists to increase their awareness and level of comfort with the atraumatic LP technique.
Vitreous humor diffusion measurements from diffusionweighted imaging in idiopathic intracranial hypertension
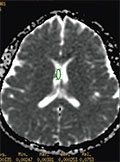
Background - Idiopathic intracranial hypertension is a disease with uncertain etiology. It is not caused by an intracranial mass lesion or hydrocephalus and is characterized by abnormal elevation of intracranial pressure and normal composition of the cerebrospinal fluid. The orbita and intracranial area are closely related anatomically. Elevated intracranial pressure can be transmitted to the orbita through the cerebrospinal fluid around the optic nerve sheath changes at the vitreous humor on diffusion-weighted imaging have not been systemically studied in idiopathic intracranial hypertension. Purpose - The purpose of this study was to investigate diffusion changes in the vitreous humor in patients with intracranial hypertension. Methods - In this retrospective study, 25 patients with papilledema and who had been definitively diagnosed with idiopathic intracranial hypertension and 20 control participants were evaluated. Control subjects and patients were scanned with a 1.5 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging. Apparent diffusion coefficient maps were obtained from diffusion-weighted imaging with a b value of 1000 s/mm2 and apparent diffusion coefficient values were automatically calculated. These images were obtained by a radiologist who was blinded to the details of the study for center of each vitreous humor and the body of lateral ventricle. The mean apparent diffusion coefficient values of each vitreous humor and the body of the lateral ventricle were calculated for each group (control group and patients) and quantitative comparisons were performed. Results - There were no statistically significant differences in mean apparent diffusion coefficient values of the right vitreous humor, left vitreous humor and the body of the lateral ventricle between the patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension and the control group (p=0.766, p=0.864, p=0.576, respectively). Discussion - Vitreous humor is a closed system and has no direct relationship with the cerebrospinal fluid or cerebral tissue and although morphological changes occur in the orbital structures, including the optic disk and optic nerve in idiopathic intracranial hypertension, the indirect effects of these changes on the vitreous humor may be too subtle to measure. Conclusion - We did not find a significant difference in the mean apparent diffusion coefficient value of the vitreous humor between the patients with idiopathic intracranial hypertension and the control group. However, future studies will be necessary to determine if changes in the vitreous humor can be used to diagnose intracranial hypertension.
Could red cell distribution width and mean platelet volume be a predictor for lumbar disc hernias?
Background - Lumbar disc herniation (LDH) causes major disabilities worldwide. Several studies in the literature had reported the correlation between radiculopathy and inflammatory markers. Mean platelet volume (MPV), red cell distribution width (RDW) and neutrophil to lymphocyte (N/L) ratio are parameters of hemogram which have been found to be associated with inflammatory conditions. Purpose - Since inflammation has an important role in lumbar disc hernias, and RDW, MPV and N/L ratio are also known to be in correlation with inflammation, we have investigated these parameters of the patients with lumbar disc hernias and compared them with the results of the healthy subjects. Methods - Our study group was composed of patients with lumbar disc hernia, whereas the control group was consisted of healthy volunteers whom visited our outpatient clinics for a routine check-up. Patient characteristics and hemogram parameters of the study cohort were obtained from computerized database system of our institution. SPSS software (SPSS 15.0 for Windows, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for the analysis. Results - There was no significant difference between study and control groups in terms of WBC, neutrophil count, lymphocyte count, neu\lym ratio, Hb, Htc, MCV, and PLT levels (all p>0.05). RDW was significantly increased in study group [15.6 (12.3-22.5)] when compared to control group [14.5(11.9-16.3)] (p=0.004). And MPV in the study group [9.25 (6.38-14.5)] was also significantly increased in comparison to the control subjects [8.8 (6-10.1)] (p=0.013). Discussion - In this retrospective study, we found that, RDW and MPV values in hemograms were increased in patients with lumbar disc herniation when compared to the control group. Conclusions - We suggest that, elevated RDW and MPV may help physicians in decision taking to order radiological imagings in patients with symptoms which can be associated with possible LDH diagnosis. However, for the sake of precision, prospective studies with larger populations are needed.
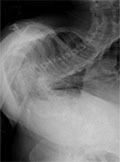
Unilateral thalamic infarction causing downward gaze palsy in a patient with uncorrected tetralogy of fallot: a case report
Introduction - Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is the most common form of cyanotic congenital heart disease (CHD). Adults with surgically uncorrected forms of this condition are extremely rare, since operation is recommended in childhood to prevent cyanosis. Cyanotic CHD increases the risk of thromboembolic events. An endothelial dysfunction caused by chronic hypoxia and shear stress due to rheological alterations with a platelet dysfunction appear to be the explanation behind this finding. Paramedian thalamic infarction causing vertical gaze palsy without midbrain involvement is an infrequent finding. We report here a rare case of a patient with untreated TOF, who suffered a left-sided unilateral thalamic infarction presenting as downward gaze palsy and diplopia. Case presentation - A 44-year-old women complained of sudden onset diplopia and vertigo. Neurological examination revealed a downward gaze palsy with other symptoms related to a vertebrobasilar territory circulatory disturbance. The MRI scan revealed an acute infarction, 8 mm in diameter in the left medial thalamic region without midbrain involvement. Discussion - Adults with uncorrected forms of TOF are extremely uncommon, and descriptions of stroke in these patients are therefore rarities. We set out to give a concise survey of the literature regarding TOF patients with stroke. Conclusion - We present a rare case of unilateral thalamic infarction causing downward gaze palsy in an adult patient with uncorrected TOF. Cyanotic CHD is regarded as one of the risk factors of stroke. Besides other pathologic conditions, ischaemic stroke at an early age should raise the suspicion of a cardioembolic origin and, in rare cases, might result from cyanotic CHD.
[Ketamine administration in case of severe, therapy resistant depressed patient, case report]
[Objective - In our case report we present the treatment of a female patient suffering from therapy resistant depression. This procedure is not in practice in Hungary at present, the aim of our work to reproduce the findigs of international studies in domestic circumstances. Matter - Major depression is a common, chronic and severe mental disorder, with 16.2% lifetime prevalence. Many international randomized, placebo controlled trials found administration of ketamine infusion effective in depressed patients. Methods - Since ketamine is an anesthetic agent, its administration was performed in the post-operative monitoring room of our hospital operating-room, supervised by an anesthesiologist. According to formerly published data, a dose of 0.5 mg/kg of body weight was administered intravenously in 40 minutes by perfusor. The drug was administered in a same manner fifteen days later. Subject - The patient was admitted to our inpatient ward with severe depression. During two months of combined antidepressant therapy her condition has not improved significantly. Approval for off label drug indication was granted with urgency by the National Institute of Quality and Organizational Development in Healthcare and Medicines. Results - During the two treatments the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale 21 items rating scale score was reduced to 8 from the baseline 28, the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale score was reduced to 6 from 25, Beck Depression Inventory was reduced to 9 from 20. Upon administration of the drug no severe adverse event was detected, the mild dissociative state related to ketamine was ceased in a short period of time. Discussion - With administration of 0.5 mg/kg ketamine the authors managed to achieve rapid improvement in a therapy resistant depressed patient, without permanent side effects. Our future plan is to repeat the use of the drug within a double-blind, placebo controlled trial in order to prove its efficacy in hospital settings. ]
NMDA-receptor associated encephalitis in a woman with mature cystic ovarian teratoma
Introduction - N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA-R) antibody-associated encephalitis has been reported in the international neurological literature to be associated with mature or immature ovarian teratomas (OTs). However, few cases of encephalitis were diagnosed in Hungary. In 2011 Hollody et al. described the first case of anti-NMDA receptor associated encephalitis in Hungary. Objective - Our aim was to present a case of NMDA-R antibody-mediated encephalitis in a woman with OT thereby providing information facilitating diagnosis of OT in women, who present with symptoms of encephalitis. Case - We report the case of a 25 year-old women, who developed NMDA-R -antibody associated autoimmune encephalitis and who displayed confusion, disorientation, a behavioural disturbance with agitation and features of paranoia and at least one reported generalized tonic clonic seizure and orofacial dyskinesia. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a functional ovarian cyst measuring 3.3 cm, which was removed surgically and demonstrated histologically to be a mature cystic OT. The serum was positive for antibodies to NMDA receptors. Following intravenous immunoglobulin treatment, oophorectomy and a 5-day course of plasma exchange, followed by corticosteroid and azathioprine immunosuppressive therapy, the patient displayed a significant clinical improvement. Conclusion - Cystic teratomas are common benign ovarian lesions in women of reproductive age. Although the association of OTs and NMDA-R antibody-associated encephalitis has been described in the international neurological literature, this relationship needs to be considered from on the interdisciplinary aspect by the health care providers.
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.