The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Ca&Bone - 2003;6(02)
Content
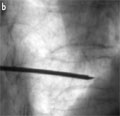
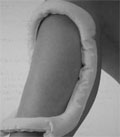
[Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures]
[Percutaneous vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that is increasingly applied for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures. The authors discuss its indications, patient selection criteria, the issue of diagnostic imaging, the technique of the procedure, its potential complications, review the literature on post-procedure pain relief, and briefly present their own experience in the treatment of osteoporotic fractures. Vertebroplasty is indicated for patients with severe, persistent, often incapacitating focal back pain not responding to standard medical therapy, which is related to the collapse of one or more vertebral bodies. Patients selected carefully by the clinical symptoms and the imaging studies usually respond promptly to the treatment, experience significant pain relief, improvement of the quality of life, and an increase in mobility.Vertebroplasty is a safe procedure with relatively low complication rates.The potential neurological complications, however, necessitate an instantly available neurosurgical background.]
[The effect of intranasal salmon calcitonin therapy on bone mineral density in idiopathic male osteoporosis without vertebral fractures]
[INTRODUCTION -The aim of this study was to examine the effect of intranasal salmon calcitonin therapy on bone mineral density in idiopathic male osteoporosis without vertebral fractures. MATERIALS - The randomised, prospective, controlled trial involved 71 male patients (mean age 59±6 years) suffering from idiopathic osteoporosis (lumbal spine and femoral neck T-score <-2.5) without vertebral deformity. Study design: Treatment protocol: Patients in the control group (n=31) received 400 IU Vitamin D + 1000 mg elemental calcium daily while the treatment group (n=40) received 400 IU Vitamin D, 1000 mg elemental calcium and 200 IU calcitonin nasal spray daily, by an intermittent monthly dose. METHODS - 1. Osteodensitometry: lumbar spine (L2-4) and femoral neck were measured by dual photon absorptiometry (LUNAR DPX-L, USA), whereas non-dominant radius was measured by single photon absorptiometry (NK 364, Gamma, Hungary). 2. Roentgenomorphorphometry was done onthoracic IV to lumbar IV spines and deformity indeces were calculated. The treatment period was 18 months. Examinations were performed at baseline and at the end of treatment.The primary end-point was the change of bone density measured by osteodensitometry. Secondary end-points included the side effects of medication. RESULTS - Nasal calcitonin was associated with significant increase in bone mineral density at the lumbar spine (+3.5±4.3% vs. +0.83±6.4%, p=0.04) and the femoral neck (+3.2±3.9% vs. -0.68±5.7%, p=0.004). No significant difference was observed at the radius between the treatment groups (+1.4±8.8% vs. +1.4±10.9%, p=0.98). No osteoporotic fractures occurred in the treated group, but there were 3 fractures in the control group. Treatment was well tolerated with no premature discontinuations nor significant side effects compared to the control group. CONCLUSION - 200 IU salmon calcitonin nasal spray used daily, intermittently proved to be an effective and safe therapy in male idiopathic osteoporosis.]
[Results obtained by pulsed electromagnetic field therapy in delayed healing or pseudoarthrosis of various fractures]
[INTRODUCTION - Delayed healing or the development of pseudoarthrosis after a conservatively or surgically treated fracture significantly prolongs the time of patient recovery and rehabilitation.The aim of the study was to investigate the influence of pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) therapy on delayed fracture healing or pseudoarthrosis in fractures of various long bones. PATIENTS AND METHODS - Twenty-one patients with abnormal fracture healing were treated ambulatorily a mean of 8.7 months after the injury with PEMF by a Biostim device (IGEA, Italy) for a mean of seven weeks. RESULTS - Overall, fracture healing was established in 15 patients, which corresponds to a recovery rate of 71.4%. By excluding the two patients, however, in whom bone restoration was inhibited by mechanical factors, healing rate increases to 78.9%. Pain intensity decreased substantially; function and endurance of the limb improved in every patient. CONCLUSIONS - These results as well as international data justify the need for wide-spread application of biophysical bone healing enhancement methods in Hungary, the first step of which is to popularize it among clinicians.]
[Biophysical enhancement of bone healing in the orthopaedic and traumatologic patients]
[Biophysical enhancement of bone healing in the orthopaedic and traumatologic patients]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.