The eLitMed.hu medical portal uses computer cookies for convenient operation. Detailed information can be found in the Cookie-policy.
Lege Artis Medicinae - 2017;27(08-09)
Content
[United Nations program to reduce premature cardiovascular mortality by 2025 and the estimation of the success of the program]
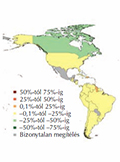
[Worldwide surveys show that cardiovascular (CV) mortality is the decisive element of total mortality. Between 1990 and 2013, the absolute number of CV deaths increased by 40.8%. Within this, ischemic heart disease (IHD) and stroke, such as the two main elements of mortality, have also increased to such an extent. Compared to the increase in absolute deaths, the age-standardized mortality rate per 100,000 population declined by 21.9%. The cause of the paradox is the development of therapy and the increase in the average age of the population. What is decisive for the lost life years (YLL) in CV cause of deaths IHD is moved from 4th to 1st place, stroke from 5th to third. This change is typical in the most regions of the world, including Central Europe and, above all, Hungary. The following factors contribute to increasing IHD and stroke mortality: smoking, hypertension, obesity, physical inactivity, diabetes. In 2011, the United Nations Conference on Communicable Diseases a uniform resolution was made, that it is a key objective for all nations to reduce their premature mortality by 25% in 2025. The CV diseases have been highlighted in a separate program and their name was “Heart of 25 by 25”. The main objective is to reduce the of premature CV mortality (probability of dying between 30 and 70 years). The target consists of main points: 30% reduction in smoking, 25% reduction in the prevalence of high blood pressure, halt the rise in obesity and diabetes type 2. Worldwide estimations were made on what would be expected in 2025 when the program was successful or unsuccessful. If the current trend remains then 30% in women and 34% in men would increase premature mortality. If all factors are influenced, then the increase will be only 1% for women and a reduction by 6% for men for developed countries, a reduction in both sexes would exceed 20%.]
[Cardiovascular screening and risk stratification]
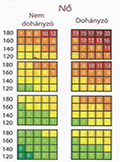
[Cardiovascular diseases are still leading cause of death in developed countries. A possible background, atherosclerosis, might appear even in childhood, and deteriorate during the years without any symptoms. The cardiovascular prevention is a complex activity, which can be observed in population or/and in individual level. The conventional screening means the assessment of higher cholesterol level, blood pressure or other risk factors in healthy population without symptoms. The point of clinical risk evaluation is to find patient with high cardiovascular risk and consequentially with the necessity of intensive preventive strategy. For the right cardiovascular screening and adequate evaluation of the risk, it is needed that the doctors who frequently meet with the population execute the above-mentioned risk assessment. Therefore doctors, nurses, and education for preventive aspect would is needed, as education is important to decrease cardiovascular mortality for those patients that were categorized as a high-risk group.]
[Dementia and pseudodementia - depression as a risk factor of dementia]
[Dementia and depression have the highest annual costs for brain disorders (mental and neurologic disorders) in Europe. The prevalence of these disorders is very high in the old age. The depression is common and an underrecognized part of the dementia syndrome because of similar symptomatology and the comorbidity. The correct differential diagnosis is important in the therapeutic approach. The pseudodementia of depression can be improved by antidepressants. The author reviewed the symptomatologic and neurobiological connection of these two disorders.]
[Effective fulvestrant treatment of indolent breast cancer in a patient with low compliance - a case report]
[In the explosive development of treatment of oncological patients, there are still patients who are not always cooperative even in their own treatment. The case report exemplifies that even in this case the endocrine treatment has its place in the hormone receptor positive breast cancer. ]
[Advance directive]
[In the first step the work defines the institution of advance directive, places advance directive in the context of advance care planning, and demonstrates the advantages of advance care planning. Then the forms of the advance directive are presented and related Hungarian health care sections are interepreted in the context of these back-ground conditions. In the third step decision making capacity is defined, its standards are set out, the role of substituted decision maker is delineated. In the fourth step accumulated experience with living will is demonstrated and the possible alternatives concerning the future of living will are provided: the elimination of the living will part of the institution from health care or its continued application after substantial revision. METHODS - Analytic presentation after systematic review of the literature on the topic. RESULTS - Significant experience has been accumulated since the implementation of advance directive. In light of experience two attitudes have been chrystallized regarding the future of the institution: one takes the side of the elimination of the living will part of the institution from health care, the other recommends its revised application. CONCLUSION - The American and Hungarian experiences with advance directive recommend the review of the Hungarian institution of advance directive. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
[Headache registry in Szeged: Experiences regarding to migraine patients]2.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The new target population of stroke awareness campaign: Kindergarten students ]3.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey5.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]1.
2.
Clinical Oncology
[Pancreatic cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up]3.
Clinical Oncology
[Pharmacovigilance landscape – Lessons from the past and opportunities for future]4.
5.