[A New Perspective in Dentistry: Teledentistry in the 21st Century]
GULYÁS Judit1, KIS-GYÖRGY Rita2
MAY 03, 2024
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2024;37(2)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55608/nover.37.0005
Review
GULYÁS Judit1, KIS-GYÖRGY Rita2
MAY 03, 2024
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice - 2024;37(2)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.55608/nover.37.0005
Review
Szöveg nagyítása:
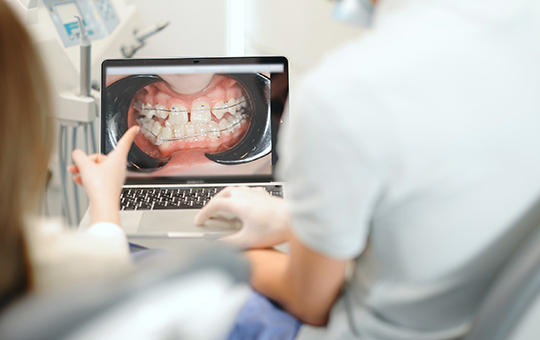
[Technical progress in the modern age is rapidly expanding in the fields of health and medicine. Telemedicine is taking off, and global digitalisation is opening up new horizons in all segments of healthcare. Telemedicine has been evolving for decades and can provide a relevant toolkit for preventive and curative care, patient monitoring, and interactions between professionals. Its role is essential for the prevention and better management of common dental diseases. However, in addition to its many advantages, it also has limitations that challenge both professionals and patients visiting the care system.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The high blood pressure disease is one of the primary risk factors for the development of other cardiovascular diseases. The aim of the present study was to assess the medication habits, sleep quality, and quality of life of patients aged 45 and older living with hypertension.
Our study was a quantitative descriptive cross-sectional survey conducted in 2022 in the form of an online questionnaire among patients aged 45 and older suffering from hypertension (n=143). The data collection tools included the Morisky Medication Adherence Scale (8 items), the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, EQ-5D-5L, and a self-designed questionnaire.
Lower age was associated with higher levels of medication adherence (R=-0.36; p=0.024). Patients who regularly visited their general practitioner showed more consistent medication intake (p=0.048). Adequate sleep quality positively influenced the quality of life (p<0.001).
Regular visits to the general practitioner not only facilitate medication adherence but also provide an excellent opportunity for patient education and health promotion. Therefore, it has paramount importance to draw the attention of hypertensive patients to the role of regular check-ups with their general practitioner, which can contribute to the prevention of complications arising from hypertension.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Accidental injuries to milk teeth are a common occurrence in young children. Many people – if the injury does not seem serious – do not even consider it a serious injury, because „it’s just a milk tooth” and „another one will grow in its place”. Because of these misconceptions, the aim of this article is to raise awareness of the forms and possible consequences of traumatic injuries to milk teeth and to familiarise health professionals with the treatment of these injuries, thus highlighting the importance of dental care for children, even in the most mildly apparent cases, to protect the germs of the teeth to be eroded.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Diabetes affects the whole body, altering fundamental metabolic processes. The number of people with diabetes is gradually increasing, with a growing proportion of younger and younger people affected. While significant lifestyle changes are needed to manage diabetes, some form of medication is also essential. Often, only the importance of exercise and diet is brought to patients’ attention by professionals, overlooking the importance of oral prevention. A number of oral conditions (e.g. dry mouth, gingivitis) can occur in people with diabetes as a result of poor oral hygiene. It is important to raise awareness of these conditions and how to prevent them at all levels of healthcare.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[ ]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[ ]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[The use of fluorides is one of the most important areas of dental prevention. It has many beneficial effects on teeth, and it is worth using them starting from childhood. It has an important role in caries prevention and in ensuring the strength of the enamel. However, we must pay attention to take fluoride into our body in moderation. If we don’t act accordingly, we can damage the condition of the teeth and the structure of the bones, to which we should pay special attention during childhood. Fluorosis can be prevented by attention, but adequate information is essential for this, which can be provided by both dentists and dental hygienists.]
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[In addition to the joyful nature of pregnancy, this condition uses a great drain to the organization of women, and the oral cavity and teeth are no exceptions. Neglected teething poses several dangers not only to the mother, but to the embryo as well. The mother may develop bleeding gums, inflammation, tooth decay among other problems, and in the foetus may have dental malformations, infection, premature birth or even miscarriage. Researches have shown that pregnant women who are more often attended to dental screening brought a newborn baby into the world with higher weight and the chances of the perinatal complications were on a lower level than those women who were rarely or not tested at all. For this reason, it is an important issue to acutely look after the dental check during pregnancy, not only in dental care but all levels of health care and by almost all professionals with whom the pregnant one meets during that nine months.]
Clinical Neuroscience
[COVID-19 has made providing in-person care difficult. In most countries, including Hungary, telemedicine has partly served as a resolution for this issue. Our purpose was to explore the effects of COVID-19 on neurological care, the knowledge of neurology specialists on telemedicine, and the present state of telecare in Hungary, with a special focus on Parkinson’s disease (PD). Between July and October 2021, a nationwide online survey was conducted among actively practicing Hungarian neurology specialists who were managing patients with PD. A total of 104 neurologists were surveyed. All levels of care were evaluated in both publicly funded and private healthcare. Both time weekly spent on outpatient specialty consultation and the number of patients with PD seen weekly significantly decreased in public healthcare, while remained almost unchanged in private care (p<0.001); higher portion of patients were able to receive in-person care in private care (78.8% vs. 90.8%, p<0.001). In telecare, prescribing medicines has already been performed by the most (n=103, 99%). Electronic messages were the most widely known telemedicine tools (n=98, 94.2%), while phone call has already been used by most neurologists (n=95, 91.3%). Video-based consultation has been more widely used in private than public care (30.1% vs. 15.5%, p=0.001). Teleprocedures were considered most suitable for monitoring progression and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and evaluating the need for adjustments to antiparkinsonian pharmacotherapy. COVID-19 has had a major impact on the care of patients with PD in Hungary. Telemedicine has mitigated these detrimental effects; however, further developments could make it an even more reliable component of care.]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[Parkinson’s disease is the elderly people’s condition which increases the risk of infections in the upper airways in its advanced stages. Specific diseases (as hypertension, diabetes mellitus), older age and the male sex are significantly worsening the course of COVID-19. It would be challenging to examine parallel these diseases, since they are raising two important questions. First, if Parkinson’s disease be a risk factor of COVID-19 morbidity and mortality. Secondly, how the COVID-19 pandemic can influence the Parkinson’s disease patients. The authors are seeking answers to these questions based on the published results in the topic concerned.]
Lege Artis Medicinae
[We aim to review the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on epilepsy and epilepsy-care. While the virus has no specific link with epilepsy, it may affect the nervous system both directly and indirectly, leading to seizures in several ways. The hyper-coagulable state occurring with the infection may cause strokes leading to seizures. The infection may first manifest in the form of disturbances of consciousness and behaviour, seizures, and even status epilepticus. The interactions of antiviral/antiepileptic drugs need to be taken into account during treatment. The hypercoagulable state induced by COVID-2 infection may cause stroke, which leads to seizures. The infection can occur also as an impaired consciousness of non-epileptic origin. Interactions of antiviral/antiepileptic drugs have also to be taken into account. The pandemic itself as well as quarantines and social distancing may cause anxiety and insomnia, challenge continuous antiepileptic supply; each one carrying the risk of seizing. Young epilepsy patients with learning disabilities and mental health issues are most vulnerable, justifying their hyper-protection. The danger of infection has highlighted the role of telemedicine. Internet-based video communication may ensure full care for chronic patients. Those methods favour bested patients with higher education. Epilepsy does not increase directly the risk of infection, but its comorbidities may worsen the course of the disease. Brain lesions and hypoxia, stress, insomnia and fever joining the infection increase seizure susceptibility. Because the danger of infection made telemedicine an essential tool of patient care, education and better computer supply for those in need is crucial. ]
1.
Clinical Neuroscience
Is there any difference in mortality rates of atrial fibrillation detected before or after ischemic stroke?2.
Clinical Neuroscience
Factors influencing the level of stigma in Parkinson’s disease in western Turkey3.
Clinical Neuroscience
[The effects of demographic and clinical factors on the severity of poststroke aphasia]4.
Clinical Neuroscience
Neuropathic pain and mood disorders in earthquake survivors with peripheral nerve injuries5.
Journal of Nursing Theory and Practice
[Correlations of Sarcopenia, Frailty, Falls and Social Isolation – A Literature Review in the Light of Swedish Statistics]1.
2.
3.
4.
5.